Growing protectionism and worsening international cooperation could badly damage the world economy, the International Monetary Fund said. Its report, released on the eve of the Davos summit — a paean to free trade and global integration — argues that poorer countries would be hit harder than rich ones. The projections add to continued gloom over economic prospects worldwide, with economists still predicting a recession as likely, despite signs of slowing inflation and hopes that China’s abandonment of zero-COVID could boost growth. [Confronting Fragmentation Where It Matters Most: Trade, Debt ... – IMF]
- Fragmentation could make it even more difficult to help many vulnerable emerging and developing economies that have been hard hit by multiple shocks
- Longer-term, just 40% of people surveyed worldwide believe they and their families will be better off in five years, down from 50% a year ago.
As policymakers and business leaders gather at the World Economic Forum in Davos, they are facing a Gordian knot of challenges .
From the global economic slowdown and climate change to the cost-of-living crisis and high debt levels: there is no easy way to cut through it. Added to this are geopolitical tensions that have made it even more difficult to address vital global issues.
Indeed, even as we need more international cooperation on multiple fronts, we are facing the specter of a new Cold War that could see the world fragment into rival economic blocs. This would be a collective policy mistake that would leave everyone poorer and less secure.
It would also be a stunning reversal of fortune. After all, economic integration has helped billions of people become wealthier, healthier, and better educated. Since the end of the Cold War, the size of the global economy roughly tripled, and nearly 1.5 billion people were lifted out of extreme poverty. This peace and cooperation dividend should not be squandered.
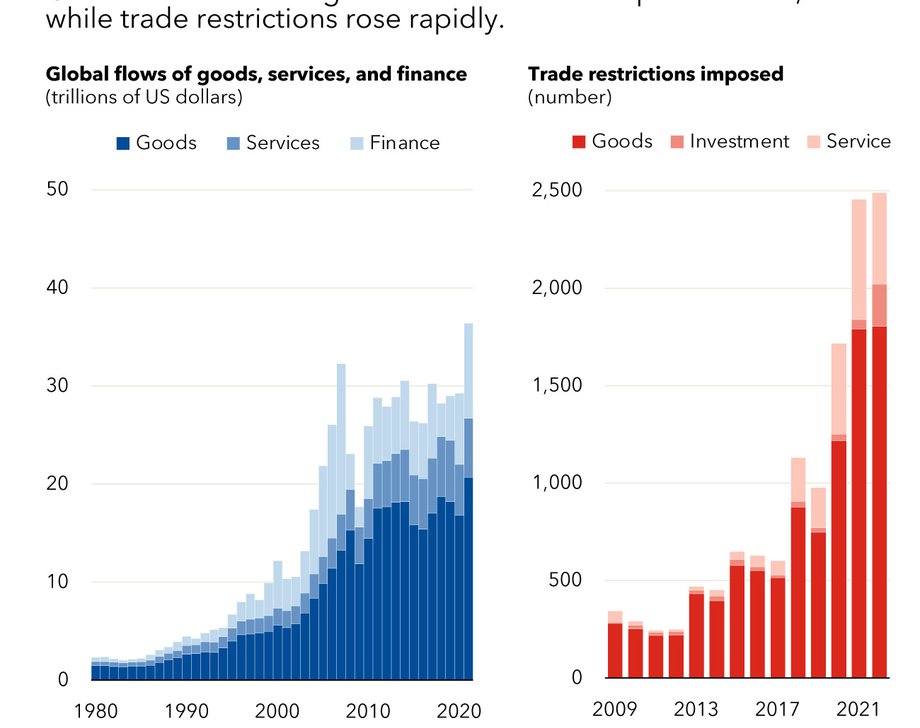
Rising fragmentation risks
And yet, not everyone has benefited from global integration. Dislocations from trade and technological change have harmed some communities. Public support for economic openness has declined in several countries. And since the global financial crisis, cross-border flows of goods and capital have been leveling-off.
But that’s only part of the story. Trade tensions between the world’s two largest economies have been rising amid a global surge in new trade restrictions. Meanwhile, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has caused not only human suffering, but also massive disruptions of financial, food, and energy flows across the globe.
Of course, countries have always placed some restrictions on trade in goods, services, and assets for legitimate economic and national security considerations. Supply chain disruptions during the COVID-19 pandemic have also increased the focus on economic security and making supply chains more resilient.
Since the outbreak, mentions in companies’ earnings presentations of reshoring, onshoring, and near-shoring have increased almost ten-fold. The risk is that policy interventions adopted in the name of economic or national security could have unintended consequences, or they could be used deliberately for economic gains at the expense of others.
That would be a dangerous slippery slope towards runaway geoeconomic fragmentation.
Estimates of the cost of fragmentation from recent studies vary widely. The longer-term cost of trade fragmentation alone could range from 0.2 percent of global output in a limited fragmentation scenario to almost 7 percent in a severe scenario—roughly equivalent to the combined annual output of Germany and Japan. If technological decoupling is added to the mix, some countries could see losses of up to 12 percent of GDP.
Yet, according to new IMF staff analysis, the full impact would likely be even larger, depending on how many channels of fragmentation are factored in. In addition to trade restrictions and barriers to the spread of technology, fragmentation could be felt through restrictions on cross-border migration, reduced capital flows, and a sharp decline in international cooperation that would leave us unable to address the challenges of a more shock-prone world.
This would be especially challenging for those who are most affected by fragmentation. Lower-income consumers in advanced economies would lose access to cheaper imported goods. Small, open-market economies would be hard-hit. Most of Asia would suffer due to its heavy reliance on open trade.
And emerging and developing economies would no longer benefit from technology spillovers that have boosted productivity growth and living standards. Instead of catching up to advanced economy income levels, the developing world would fall further behind.
Focus on what matters most: trade, debt, and climate action
So, how can we confront fragmentation? By taking a pragmatic approach. This means focusing on areas where cooperation is essential, and delay is not an option. It also means finding new ways to achieve common objectives. Let me highlight three priorities:
First, strengthen the international trade system.
In a global economy beset with low growth and high inflation, we need a much stronger trade engine. Trade growth is expected to decline in 2023, which makes it even more critical to roll back the distortionary subsidies and trade restrictions imposed in recent years.
Strengthening the role of trade in the global economy begins with vigorous World Trade Organization reform and by concluding WTO-based market-opening agreements. But finding agreement on complex trade issues remains challenging, given the diverse World Trade Organization membership, increasing complexity of trade policy, and heightened geopolitical tensions.
In some areas, plurilateral agreements, among subsets of WTO members, can offer a path forward. Take the recent agreement on regulatory cooperation in service industries—from finance to call centers—which can reduce the cost of providing services across borders.
We also need to be pragmatic about strengthening supply chains. To be clear, while most supply chains have been resilient, recent disruptions to food and energy supplies have raised legitimate concerns. Still, policy choices such as reshoring could leave countries more vulnerable to shocks. IMF research shows that diversification can cut potential economic losses from supply disruptions in half.
Meanwhile, countries should carefully weigh the costs, at home and abroad, of national security measures on trade or investment. We also need to develop guardrails to protect the vulnerable from unilateral actions. A good example is the recently agreed requirement to exclude from food export restrictions the exports to humanitarian agencies such as the World Food Program.
But these efforts, while important, aren’t enough. We also need better policies at home, from improving social safety nets, to investing in job training, to increasing worker mobility across industries, regions, and occupations. This is how we can ensure that trade works for all.
Second, help vulnerable countries deal with debt.
Fragmentation could make it even more difficult to help many vulnerable emerging and developing economies that have been hard hit by multiple shocks. Take one particular challenge that many countries face: debt. Fragmentation will make it harder to resolve sovereign debt crises, especially if key official creditors are divided along geopolitical lines.
About 15 percent of low-income countries are already in debt distress and an additional 45 percent are at high risk of debt distress. Among emerging markets, about 25 percent are at high risk and facing default-like borrowing spreads.
There are signs of progress on the Group of Twenty’s Common Framework for debt treatment: Chad recently reached an agreement with its official and private creditors; Zambia is progressing toward a debt restructuring; and Ghana just became the fourth country to seek treatment under the Common Framework, sending a signal that it is seen as an important pathway for debt resolution. But official creditors have a lot more work to do.
Countries seeking debt restructuring under the Framework will need greater certainty on processes and standards, as well as shorter and more predictable timelines. And we need to improve processes for countries not covered by the Framework. To support these improvements, the IMF, World Bank and Indian G20 presidency are working with borrowers and public and private creditors to quickly establish a global sovereign debt roundtable, where we can discuss current shortcomings and make progress to address them.
These and other pragmatic actions, such as further progress on majority voting provisions in sovereign loans and climate resilient debt clauses, can help improve debt resolution. That would reduce economic and financial uncertainty, while helping countries get back to investing in their future.
Third, step up climate action.
Collective action is just as vital to address the climate crisis. Just last year, we saw climate disasters on all five continents, with $165 billion in damages in the United States alone. It shows the massive economic and financial risks of unmitigated global warming.
But last year also brought some good news. The agreement at COP27 to set up a loss and damage fund for the most vulnerable countries shows that progress is possible with enough political will. Now we must take further pragmatic steps to cut emissions and curb fossil fuels.
One potential game changer could be an international carbon price floor among major emitters. It would focus on carbon pricing or equivalent measures in an equitable process that would complement and reinforce the Paris Agreement. Or consider the "just energy transition partnerships" between groups of donors and countries such as South Africa and Indonesia.
We also need to step up climate finance to help vulnerable countries adapt. Innovative use of public balance sheets—such as credit guarantees, equity and first-loss investments—can help mobilize billions of dollars in private financing.
And, of course, we need better data around climate projects: harmonized disclosure standards and principles will help, as will taxonomies to align investments to climate goals.